Edge
SuperMQ IoT platform provides services for supporting management of devices on the edge. Typically, IoT solution includes devices (sensors/actuators) deployed in far edge and connected through some proxy gateway. Although most devices could be connected to the SuperMQ directly, using gateways decentralizes system, decreases load on the cloud and makes setup less difficult. Also, gateways can provide additional data processing, filtering and storage.
Services that can be used on gateway to enable data and control plane for edge:
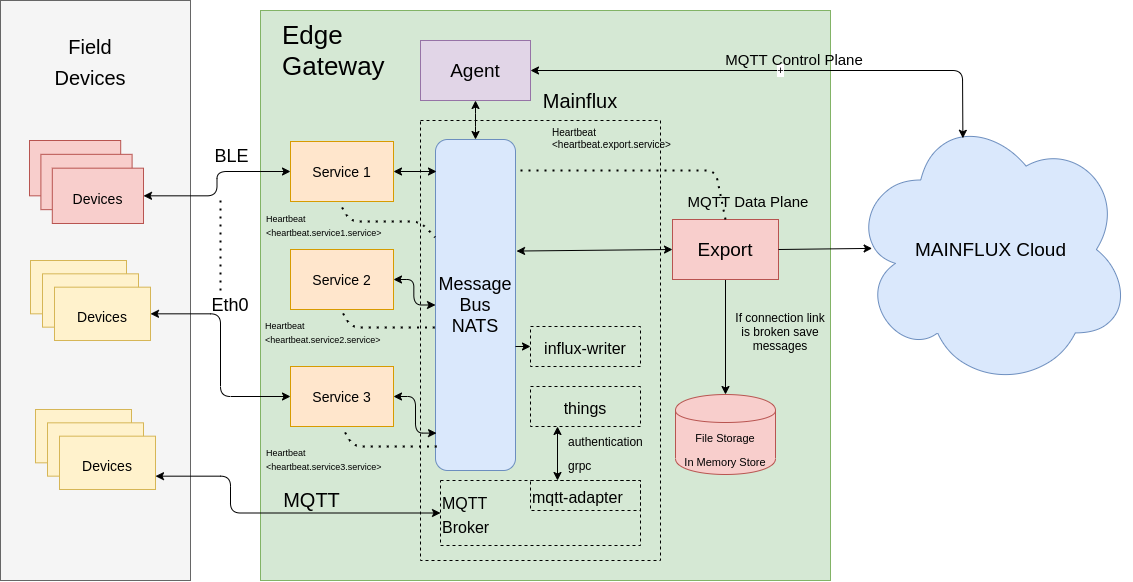 |
|---|
| Figure 1 - Edge services deployment |
Figure shows edge gateway that is running Agent, Export and minimal deployment of SuperMQ services. SuperMQ services enable device management and MQTT protocol, NATS being a central message bus as it is the default message broker in SuperMQ becomes also central message bus for other services like Agent and Export as well as for any new custom developed service that can be built to interface with devices with any of hardware supported interfaces on the gateway, those services would publish data to the message broker where Export service can pick them up and send to cloud.
Agent can be used to control deployed services as well as to monitor their liveliness through subcribing to heartbeat Message Broker subject where services should publish their liveliness status, like Export service does.
Agent
Agent is service that is used to manage gateways that are connected to SuperMQ in cloud. It provides a way to send commands to gateway and receive response via mqtt. There are two types of channels used for Agent data and control. Over the control we are sending commands and receiving response from commands. Data collected from sensors connected to gateway are being sent over data channel. Agent is able to configure itself provided that bootstrap server is running, it will retrieve configuration from bootstrap server provided few arguments - external_id and external_key see bootstraping.
Agent service has following features:
- Remote execution of commands
- Remote terminal, remote session to
bashmanaged byAgent - Heartbeat - listening to Message Broker topic
heartbeat.>it can remotely provide info on running services, if services are publishing heartbeat ( like Export) - Proxying commands to other gateway services
- Edgex SMA - remotely making requests to EdgeX endpoints and fetching results, if EdgeX is deployed.
Run Agent
Before running agent we need to provision a client and DATA and CONTROL channel. Client that will be used as gateway representation and make bootstrap configuration. If using SuperMQ UI this is done automatically when adding gateway through UI. Gateway can be provisioned with provision service.
When you provisioned gateway as described in provision you can check results
curl -s -S -X GET http://magistrala-domain.com:9013/clients/bootstrap/<external_id> -H "Authorization: Client <external_key>" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' |jq
{
"client_id": "e22c383a-d2ab-47c1-89cd-903955da993d",
"client_key": "fc987711-1828-461b-aa4b-16d5b2c642fe",
"channels": [
{
"id": "fa5f9ba8-a1fc-4380-9edb-d0c23eaa24ec",
"name": "control-channel",
"metadata": {
"type": "control"
}
},
{
"id": "24e5473e-3cbe-43d9-8a8b-a725ff918c0e",
"name": "data-channel",
"metadata": {
"type": "data"
}
},
{
"id": "1eac45c2-0f72-4089-b255-ebd2e5732bbb",
"name": "export-channel",
"metadata": {
"type": "export"
}
}
],
"content": "{\"agent\":{\"edgex\":{\"url\":\"http://localhost:48090/api/v1/\"},\"heartbeat\":{\"interval\":\"30s\"},\"log\":{\"level\":\"debug\"},\"mqtt\":{\"mtls\":false,\"qos\":0,\"retain\":false,\"skip_tls_ver\":true,\"url\":\"tcp://magistrala-domain.com:1883\"},\"server\":{\"nats_url\":\"localhost:4222\",\"port\":\"9000\"},\"terminal\":{\"session_timeout\":\"30s\"}},\"export\":{\"exp\":{\"cache_db\":\"0\",\"cache_pass\":\"\",\"cache_url\":\"localhost:6379\",\"log_level\":\"debug\",\"nats\":\"nats://localhost:4222\",\"port\":\"8172\"},\"mqtt\":{\"ca_path\":\"ca.crt\",\"cert_path\":\"client.crt\",\"channel\":\"\",\"host\":\"tcp://magistrala-domain.com:1883\",\"mtls\":false,\"password\":\"\",\"priv_key_path\":\"client.key\",\"qos\":0,\"retain\":false,\"skip_tls_ver\":false,\"username\":\"\"},\"routes\":[{\"mqtt_topic\":\"\",\"nats_topic\":\"channels\",\"subtopic\":\"\",\"type\":\"mfx\",\"workers\":10},{\"mqtt_topic\":\"\",\"nats_topic\":\"export\",\"subtopic\":\"\",\"type\":\"default\",\"workers\":10}]}}"
}
external_idis usually MAC address, but anything that suits applications requirements can be usedexternal_keyis key that will be provided to agent processclient_idis SuperMQ client idchannelsis 2-element array where first channel is CONTROL and second is DATA, both channels should be assigned to clientcontentis used for configuring parameters of agent and export service.
Then to start the agent service you can do it like this
git clone https://github.com/absmach/agent.git
make
cd build
MG_AGENT_LOG_LEVEL=debug \
MG_AGENT_BOOTSTRAP_KEY=edged \
MG_AGENT_BOOTSTRAP_ID=34:e1:2d:e6:cf:03 ./magistrala-agent
{"level":"info","message":"Requesting config for 34:e1:2d:e6:cf:03 from http://localhost:9013/clients/bootstrap","ts":"2019-12-05T04:47:24.98411512Z"}
{"level":"info","message":"Getting config for 34:e1:2d:e6:cf:03 from http://localhost:9013/clients/bootstrap succeeded","ts":"2019-12-05T04:47:24.995465239Z"}
{"level":"info","message":"Connected to MQTT broker","ts":"2019-12-05T04:47:25.009645082Z"}
{"level":"info","message":"Agent service started, exposed port 9000","ts":"2019-12-05T04:47:25.009755345Z"}
{"level":"info","message":"Subscribed to MQTT broker","ts":"2019-12-05T04:47:25.012930443Z"}
MG_AGENT_BOOTSTRAP_KEY- isexternal_keyin bootstrap configuration.MG_AGENT_BOOSTRAP_ID- isexternal_idin bootstrap configuration.
Remote execution of commands via Agent
# Set connection parameters as environment variables in shell
CH=`curl -s -S -X GET http://some-domain-name:9013/clients/bootstrap/34:e1:2d:e6:cf:03 -H "Authorization: Client <BOOTSTRAP_KEY>" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' | jq -r '.magistrala_channels[0].id'`
TH=`curl -s -S -X GET http://some-domain-name:9013/clients/bootstrap/34:e1:2d:e6:cf:03 -H "Authorization: Client <BOOTSTRAP_KEY>" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' | jq -r .magistrala_id`
KEY=`curl -s -S -X GET http://some-domain-name:9013/clients/bootstrap/34:e1:2d:e6:cf:03 -H "Authorization: Client <BOOTSTRAP_KEY>" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' | jq -r .magistrala_key`
# Subscribe for response
mosquitto_sub -d -u $TH -P $KEY -t "m/<domain_id>/c/${CH}/res/#" -h some-domain-name -p 1883
# Publish command e.g `ls`
mosquitto_pub -d -u $TH -P $KEY -t m/<domain_id>/c/$CH/req -h some-domain-name -p 1883 -m '[{"bn":"1:", "n":"exec", "vs":"ls, -l"}]'
Remote terminal
This can be checked from the UI, click on the details for gateway and below the gateway parameters you will se box with prompt, if agent is running and it is properly connected you should be able to execute commands remotely.
Heartbeat
If there are services that are running on same gateway as agent and they are publishing heartbeat to the Message Broker subject heartbeat.service_name.service
You can get the list of services by sending following mqtt message
# View services that are sending heartbeat
mosquitto_pub -d -u $TH -P $KEY -t m/<domain_id>/c/$CH/req -h some-domain-name -p 1883 -m '[{"bn":"1:", "n":"service", "vs":"view"}]'
Response can be observed on m/<domain_id>/c/$CH/res/#
Proxying commands
You can send commands to services running on the same edge gateway as Agent if they are subscribed on same the Message Broker server and correct subject.
Service commands are being sent via MQTT to topic:
m/<domain_id>/c/<control_channel_id>/services/<service_name>/<subtopic>
when messages is received Agent forwards them to the Message Broker on subject:
commands.<service_name>.<subtopic>
Payload is up to the application and service itself.
EdgeX
Edgex control messages are sent and received over control channel. MG sends a control SenML of the following form:
[{"bn":"<uuid>:", "n":"control", "vs":"<cmd>, <param>, edgexsvc1, edgexsvc2, …, edgexsvcN"}}]
For example,
[{"bn":"1:", "n":"control", "vs":"operation, stop, edgex-support-notifications, edgex-core-data"}]
Agent, on the other hand, returns a response SenML of the following form:
[{"bn":"<uuid>:", "n":"<>", "v":"<RESP>"}]
Remote Commands
EdgeX defines SMA commands in the following RAML file
Commands are:
- OPERATION
- CONFIG
- METRICS
- PING
Operation
mosquitto_pub -u <client_id> -P <client_secret> -t m/<domain_id>/c/<channel_id>/req -h localhost -m '[{"bn":"1:", "n":"control", "vs":"edgex-operation, start, edgex-support-notifications, edgex-core-data"}]'
Config
mosquitto_pub -u <client_id> -P <client_secret> -t m/<domain_id>/c/<channel_id>/req -h localhost -m '[{"bn":"1:", "n":"control", "vs":"edgex-config, edgex-support-notifications, edgex-core-data"}]'
Metrics
mosquitto_pub -u <client_id> -P <client_secret> -t m/<domain_id>/c/<channel_id>/req -h localhost -m '[{"bn":"1:", "n":"control", "vs":"edgex-metrics, edgex-support-notifications, edgex-core-data"}]'
If you subscribe to
mosquitto_sub -u <client_id> -P <client_secret> -t m/<domain_id>/c/<channel_id>/#
You can observe commands and response from commands executed against edgex
[{"bn":"1:", "n":"control", "vs":"edgex-metrics, edgex-support-notifications, edgex-core-data"}]
[{"bn":"1","n":"edgex-metrics","vs":"{\"Metrics\":{\"edgex-core-data\":{\"CpuBusyAvg\":15.568632467698606,\"Memory\":{\"Alloc\":2040136,\"Frees\":876344,\"LiveObjects\":15134,\"Mallocs\":891478,\"Sys\":73332984,\"TotalAlloc\":80657464}},\"edgex-support-notifications\":{\"CpuBusyAvg\":14.65381169745318,\"Memory\":{\"Alloc\":961784,\"Frees\":127430,\"LiveObjects\":6095,\"Mallocs\":133525,\"Sys\":72808696,\"TotalAlloc\":11665416}}}}\n"}]
Export
SuperMQ Export service can send message from one SuperMQ cloud to another via MQTT, or it can send messages from edge gateway to SuperMQ Cloud. Export service is subscribed to local message bus and connected to MQTT broker in the cloud. Messages collected on local message bus are redirected to the cloud. When connection is lost, if QoS2 is used, messages from the local bus are stored into file or in memory to be resent upon reconnection. Additonaly Export service publishes liveliness status to Agent via the Message Broker subject heartbeat.export.service
Install
Get the code:
go get github.com/magistrala/export
cd $GOPATH/github.com/magistrala/export
Make:
make
Usage
cd build
./magistrala-export
Configuration
By default Export service looks for config file at ../configs/config.toml if no env vars are specified.
[exp]
log_level = "debug"
nats = "localhost:4222"
port = "8170"
[mqtt]
username = "<client_id>"
password = "<client_password>"
ca_path = "ca.crt"
client_cert = ""
client_cert_key = ""
client_cert_path = "client.crt"
client_priv_key_path = "client.key"
mtls = "false"
priv_key = "client.key"
retain = "false"
skip_tls_ver = "false"
url = "tcp://magistrala.com:1883"
[[routes]]
mqtt_topic = "m/<domain_id>/c/<channel_id>"
subtopic = "subtopic"
nats_topic = "export"
type = "default"
workers = 10
[[routes]]
mqtt_topic = "m/<domain_id>/c/<channel_id>"
subtopic = "subtopic"
nats_topic = "channels"
type = "mfx"
workers = 10
Environment variables
Service will first look for MG_EXPORT_CONFIG_FILE for configuration and if not found it will be configured with env variables and new config file specified with MG_EXPORT_CONFIG_FILE (default value will be used if none specified) will be saved with values populated from env vars. The service is configured using the environment variables as presented in the table. Note that any unset variables will be replaced with their default values.
For values in environment variables to take effect make sure that there is no MG_EXPORT_CONFIG_FILE file.
If you run with environment variables you can create config file:
MG_EXPORT_PORT=8178 \
MG_EXPORT_LOG_LEVEL=debug \
MG_EXPORT_MQTT_HOST=tcp://localhost:1883 \
MG_EXPORT_MQTT_USERNAME=<client_id> \
MG_EXPORT_MQTT_PASSWORD=<client_secret> \
MG_EXPORT_MQTT_CHANNEL=<channel_id> \
MG_EXPORT_MQTT_SKIP_TLS=true \
MG_EXPORT_MQTT_MTLS=false \
MG_EXPORT_MQTT_CA=ca.crt \
MG_EXPORT_MQTT_CLIENT_CERT=client.crt \
MG_EXPORT_MQTT_CLIENT_PK=client.key \
MG_EXPORT_CONFIG_FILE=export.toml \
../build/magistrala-export&
Values from environment variables will be used to populate export.toml
Http port
port- HTTP port where status ofExportservice can be fetched.
curl -X GET http://localhost:8170/health
'{"status": "pass", "version":"0.12.1", "commit":"57cca9677721025da055c47957fc3e869e0325aa" , "description":"export service", "build_time": "2022-01-19_10:13:17"}'
MQTT connection
To establish connection to MQTT broker following settings are needed:
username- SuperMQ [client_id]password- SuperMQ [client_secret]url- url of MQTT broker
Additionally, you will need MQTT client certificates if you enable mTLS. To obtain certificates ca.crt, client.crt and key client.key follow instructions here or here.
MTLS
To setup MTLS connection Export service requires client certificate and mtls in config or MG_EXPORT_MQTT_MTLS must be set to true. Client certificate can be provided in a file, client_cert_path and client_cert_key_path are used for specifying path to certificate files. If MTLS is used and no certificate file paths are specified then Export will look in client_cert and client_cert_key of config file expecting certificate content stored as string.
Routes
Routes are being used for specifying which subscriber's topic(subject) goes to which publishing topic. Currently only MQTT is supported for publishing. To match SuperMQ requirements mqtt_topic must contain m/<domain_id>/c/<channel_id>, additional subtopics can be appended.
mqtt_topic-m/<domain_id>/c/<channel_id>/<custom_subtopic>nats_topic-Exportservice will be subscribed to the Message Broker subject<nats_topic>.>subtopic- messages will be published to MQTT topic<mqtt_topic>/<subtopic>/<nats_subject>, where dots in nats_subject are replaced with '/'workers- specifies number of workers that will be used for message forwarding.type- specifies message transformation:defaultis for sending messages as they are received on the Message Broker with no transformation (so they should be in SenML or JSON format if we want to persist them in SuperMQ in cloud). If you don't want to persist messages in SuperMQ or you are not exporting to SuperMQ cloud - message format can be anything that suits your application as message passes untransformed.mfxis for messages that are being picked up on internal SuperMQ Message Broker bus. When usingExportalong with SuperMQ deployed on gateway (Fig. 1) messages coming from MQTT broker that are published to the Message Broker bus are SuperMQ message. Usingmfxtype will extract payload andexportwill publish it tomqtt_topic. Extracted payload is SenML or JSON if we want to persist messages.nats_topicin this case must bechannels, or if you want to pick messages from a specific channel in local SuperMQ instance to be exported to cloud you can putchannels.<local_magistrala_channel_id>.
Before running Export service edit configs/config.toml and provide username, password and url
username- matchesclient_idin SuperMQ cloud instancepassword- matchesclient_secretchannel- MQTT part of the topic where to publish MQTT data (m/<domain_id>/c/<channel_id>is format of supermq MQTT topic) and plays a part in authorization.
If SuperMQ and Export service are deployed on same gateway Export can be configured to send messages from SuperMQ internal Message Broker bus to SuperMQ in a cloud. In order for Export service to listen on SuperMQ Message Broker deployed on the same machine Message Broker port must be exposed. Edit SuperMQ docker-compose.yml. Default Message Broker, NATS, section must look like below:
nats:
image: nats:2.2.4
container_name: magistrala-nats
restart: on-failure
networks:
- magistrala-base-net
ports:
- 4222:4222
How to save config via agent
Configuration file for Export service can be sent over MQTT using Agent service.
mosquitto_pub -u <client_id> -P <client_secret> -t m/<domain_id>/c/<control_ch_id>/req -h localhost -p 18831 -m "[{\"bn\":\"1:\", \"n\":\"config\", \"vs\":\"save, export, <config_file_path>, <file_content_base64>\"}]"
vs="save, export, config_file_path, file_content_base64" - vs determines where to save file and contains file content in base64 encoding payload:
b,_ := toml.Marshal(export.Config)
payload := base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(b)
Using configure script
There is a configuration.sh script in a scripts directory that can be used for automatic configuration and start up of remotely deployed export. For this to work it is presumed that magistrala-export and scripts/export_start are placed in executable path on remote device. Additionally this script requires that remote device is provisioned following the steps described for provision service.
To run it first edit script to set parameters
MTLS=false
EXTERNAL_KEY='raspberry'
EXTERNAL_ID='pi'
MAGISTRALA_HOST='magistrala.com'
MAGISTRALA_USER_EMAIL='edge@email.com'
MAGISTRALA_USER_PASSWORD='12345678'
EXTERNAL_KEY and EXTERNAL_ID are parameters posted to /mapping endpoint of provision service, MAGISTRALA_HOST is location of cloud instance of SuperMQ that export should connect to and MAGISTRALA_USER_EMAIL and MAGISTRALA_USER_PASSWORD are users credentials in the cloud.
Example deployment
Edge deployment
The following are steps that are an example usage of SuperMQ components to connect edge with cloud. We will start SuperMQ in the cloud with additional services Bootstrap and Provision. Using Bootstrap and Provision we will create a configuration for use in gateway deployment. On the gateway we will start services Agent and Export using previously created configuration.
Services in the cloud
Start the SuperMQ:
docker-compose -f docker/docker-compose.yml up
Start the Bootstrap service:
docker-compose -f docker/addons/bootstrap/docker-compose.yml up
Start the Provision service
docker-compose -f docker/addons/provision/docker-compose.yml up
Create user:
supermq-cli -m http://localhost:9002 users create test test@email.com 12345678
Obtain user token:
supermq-cli -m http://localhost:9002 users token test@email.com 12345678
{
"access_token": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzUxMiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJleHAiOjE2ODY3NTEzNTIsImlhdCI6MTY4Njc1MDQ1MiwiaWRlbnRpdHkiOiJqb2huLmRvZUBlbWFpbC5jb20iLCJpc3MiOiJjbGllbnRzLmF1dGgiLCJzdWIiOiI5NDkzOTE1OS1kMTI5LTRmMTctOWU0ZS1jYzJkNjE1NTM5ZDciLCJ0eXBlIjoiYWNjZXNzIn0.AND1sm6mN2wgUxVkDhpipCoNa87KPMghGaS5-4dU0iZaqGIUhWScrEJwOahT9ts1TZSd1qEcANTIffJ_y2Pbsg",
"refresh_token": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzUxMiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJleHAiOjE2ODY4MzY4NTIsImlhdCI6MTY4Njc1MDQ1MiwiaWRlbnRpdHkiOiJqb2huLmRvZUBlbWFpbC5jb20iLCJpc3MiOiJjbGllbnRzLmF1dGgiLCJzdWIiOiI5NDkzOTE1OS1kMTI5LTRmMTctOWU0ZS1jYzJkNjE1NTM5ZDciLCJ0eXBlIjoicmVmcmVzaCJ9.z3OWCHhNHNuvkzBqEAoLKWS6vpFLkIYXhH9cZogSCXd109-BbKVlLvYKmja-hkhaj_XDJKySDN3voiazBr_WTA",
"access_type": "Bearer"
}
USER_TOKEN=<access_token>
Provision a gateway:
curl -s -S -X POST http://localhost:9016/mapping -H "Authorization: Bearer $USER_TOKEN" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{"name":"testing", "external_id" : "54:FG:66:DC:43", "external_key":"223334fw2" }' | jq
{
"clients": [
{
"id": "88529fb2-6c1e-4b60-b9ab-73b5d89f7404",
"name": "client",
"key": "3529c1bb-7211-4d40-9cd8-b05833196093",
"metadata": {
"external_id": "54:FG:66:DC:43"
}
}
],
"channels": [
{
"id": "1aa3f736-0bd3-44b5-a917-a72cc743f633",
"name": "control-channel",
"metadata": {
"type": "control"
}
},
{
"id": "e2adcfa6-96b2-425d-8cd4-ff8cb9c056ce",
"name": "data-channel",
"metadata": {
"type": "data"
}
}
],
"whitelisted": {
"88529fb2-6c1e-4b60-b9ab-73b5d89f7404": true
}
}
Parameters external_id and external_key are representing the gateway. Provision will use them to create a bootstrap configuration that will make a relation with SuperMQ entities used for connection, authentication and authorization client and channel. These parameters will be used by Agent service on the gateway to retrieve that information and establish a connection with the cloud.
Services on the Edge
Agent service
Start the NATS and Agent service:
gnatsd
MG_AGENT_BOOTSTRAP_ID=54:FG:66:DC:43 \
MG_AGENT_BOOTSTRAP_KEY="223334fw2" \
MG_AGENT_BOOTSTRAP_URL=http://localhost:9013/clients/bootstrap \
build/magistrala-agent
{"level":"info","message":"Requesting config for 54:FG:66:DC:43 from http://localhost:9013/clients/bootstrap","ts":"2020-05-07T15:50:58.041145096Z"}
{"level":"info","message":"Getting config for 54:FG:66:DC:43 from http://localhost:9013/clients/bootstrap succeeded","ts":"2020-05-07T15:50:58.120779415Z"}
{"level":"info","message":"Saving export config file /configs/export/config.toml","ts":"2020-05-07T15:50:58.121602229Z"}
{"level":"warn","message":"Failed to save export config file Error writing config file: open /configs/export/config.toml: no such file or directory","ts":"2020-05-07T15:50:58.121752142Z"}
{"level":"info","message":"Client agent-88529fb2-6c1e-4b60-b9ab-73b5d89f7404 connected","ts":"2020-05-07T15:50:58.128500603Z"}
{"level":"info","message":"Agent service started, exposed port 9003","ts":"2020-05-07T15:50:58.128531057Z"}
Export service
git clone https://github.com/absmach/export.git
make
Edit the configs/config.toml setting
username- client from the results of provision request.password- key from the results of provision request.mqtt_topic- in routes set tom/<domain_id>/c/<channel_data_id>from results of provision.nats_topic- whatever you need, export will subscribe toexport.<nats_topic>and forward messages to MQTT.host- url of MQTT broker.
[exp]
cache_pass = ""
cache_url = ""
log_level = "debug"
nats = "localhost:4222"
port = "8170"
[mqtt]
ca_path = ""
cert_path = ""
host = "tcp://localhost:1883"
mtls = false
password = "3529c1bb-7211-4d40-9cd8-b05833196093"
priv_key_path = ""
qos = 0
retain = false
skip_tls_ver = false
username = "88529fb2-6c1e-4b60-b9ab-73b5d89f7404"
[[routes]]
mqtt_topic = "m/6a45444c-4c89-46f9-a284-9e731674726a/c/e2adcfa6-96b2-425d-8cd4-ff8cb9c056ce"
nats_topic = ">"
workers = 10
cd build
./magistrala-export
2020/05/07 17:36:57 Configuration loaded from file ../configs/config.toml
{"level":"info","message":"Export service started, exposed port :8170","ts":"2020-05-07T15:36:57.528398548Z"}
{"level":"debug","message":"Client export-88529fb2-6c1e-4b60-b9ab-73b5d89f7404 connected","ts":"2020-05-07T15:36:57.528405818Z"}
Testing Export
git clone https://github.com/absmach/agent.git
go run ./examples/publish/main.go -s http://localhost:4222 export.test "[{\"bn\":\"test\"}]";
We have configured route for export, nats_topic = ">" means that it will listen to NATS subject export.> and mqtt_topic is configured so that data will be sent to MQTT broker on topic c/e2adcfa6-96b2-425d-8cd4-ff8cb9c056ce/m with appended NATS subject. Other brokers can such as rabbitmq can be used, for more detail refer to dev-guide.
In terminal where export is started you should see following message:
{"level":"debug","message":"Published to: export.test, payload: [{\"bn\":\"test\"}]","ts":"2020-05-08T15:14:15.757298992Z"}
In SuperMQ mqtt service:
supermq-mqtt | {"level":"info","message":"Publish - client ID export-88529fb2-6c1e-4b60-b9ab-73b5d89f7404 to the topic: m/6a45444c-4c89-46f9-a284-9e731674726a/c/e2adcfa6-96b2-425d-8cd4-ff8cb9c056ce/export/test","ts":"2020-05-08T15:16:02.999684791Z"}